How to Run MSF Localization Module On Your Local Computer¶
1. Preparation¶
Download source code of Apollo from GitHub
Follow the tutorial to set up docker environment.
Download localization data from Apollo Data Open Platform(US only).
the localization data is a experimental dataset to verify the availability of localization. It contains localization map(local_map/), vehicle params(params/), sensor recording data(records/). The specific attributes are as follows: duration: 5 mins mileage: 3km areas: city roads in Sunnyvale weather: sunny day
2. Build Apollo¶
First check and make sure you are in development docker container before you proceed. Now you will need to build from the source.
# To make sure you start clean
bash apollo.sh clean
# Build the full system
bash apollo.sh build_opt
3. Configuring Parameters¶
In the downloaded data, you can find a folder named apollo3.5. Let’s assume the path of this folder as DATA_PATH.
3.1 Configure Sensor Extrinsics¶
cp -r DATA_PATH/params/* /apollo/modules/localization/msf/params/
The meaning of each file in the folder
ant_imu_leverarm.yaml: Lever arm value
velodyne128_novatel_extrinsics.yaml: Transform from IMU coord to LiDAR coord
velodyne128_height.yaml: Height of the LiDAR relative to the ground
3.2 Configure Map Path¶
Add config of map path in /apollo/modules/localization/conf/localization.conf
# Redefine the map_dir in global_flagfile.txt
--map_dir=DATA_PATH
This will overwrite the default config defined in global_flagfile.txt
4. Run the multi-sensor fusion localization module¶
run the script in apollo directory
cyber_launch start /apollo/modules/localization/launch/msf_localization.launch
In /apollo/data/log directory, you can see the localization log files.
localization.INFO : INFO log
localization.WARNING : WARNING log
localization.ERROR : ERROR log
localization.out : Redirect standard output
localizaiton.flags : A backup of configuration file
5. Play cyber records¶
cd DATA_PATH/records
cyber_recorder play -f record.*
The localization module will finish initialization and start publishing localization results after around 50 seconds.
6. Record and Visualize localization result (optional)¶
Record localization result¶
python /apollo/scripts/record_bag.py --start
Visualize Localization result¶
cyber_launch start /apollo/modules/localization/launch/msf_visualizer.launch
First, the visualization tool will generate a series of cache files from the localization map, which will be stored in the /apollo/cyber/data/map_visual directory.
Then it will receive the topics blew and draw them on screen.
/apollo/sensor/lidar128/compensator/PointCloud2
/apollo/localization/msf_lidar
/apollo/localization/msf_gnss
/apollo/localization/pose
If everything is fine, you should see this on screen.
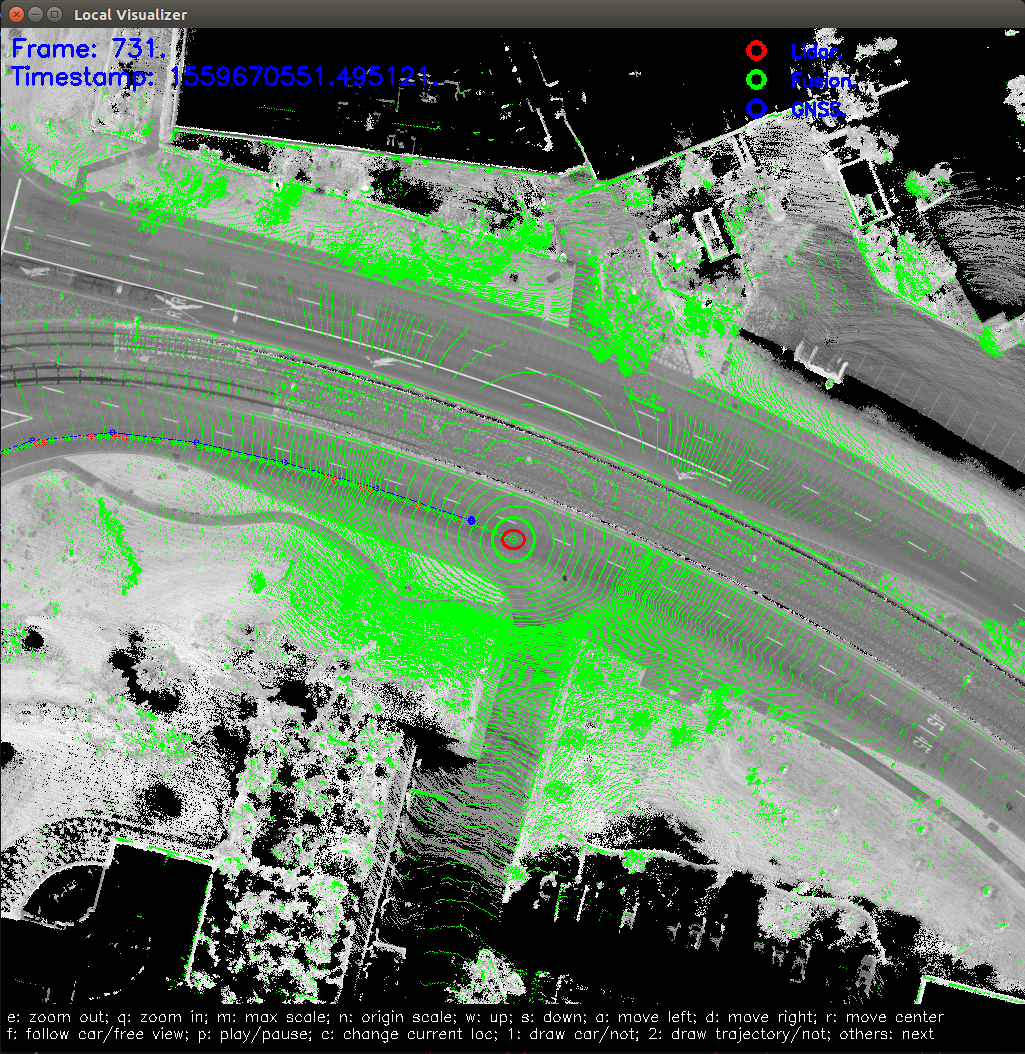
Note: The visualization tool will show up the windows after the localization module started to published localization msgs to topic /apollo/localization/pose. You can use command cyber_monitor to monitor the status of topics.
7. Stop localization module¶
If you record localization result in step 6, you will also need to end the recording process:
python /apollo/scripts/record_bag.py --stop
8. Verify the localization result (optional)¶
./scripts/msf_local_evaluation.sh OUTPUT_PATH
OUTPUT_PATH is the folder stored recording bag in step 6.
This script compares the localization results of MSF mode to RTK mode.
Note: Aware that this comparison makes sense only when the RTK mode runs well.
And we can get the statistical results like this
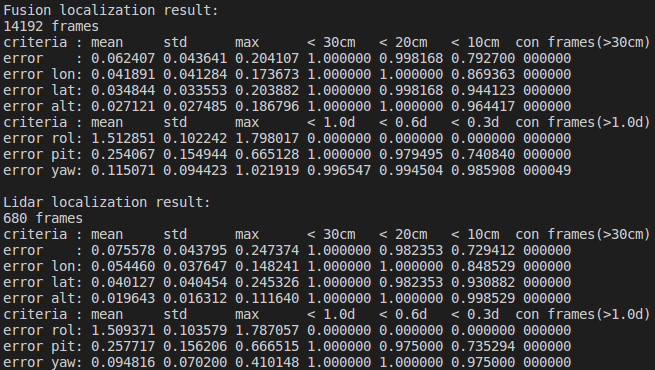
The first table is the statistical data of Fusion localization. The second table is the statistical result of Lidar localization.
The meaning of each row in the table
error: the plane error, unit is meter
error lon: the error in the car’s heading direction, unit is meter
error lat: the error in the car’s lateral direction, unit is meter
error roll: the roll angle error, unit is degree
error pit: the pitch angle error, unit is degree
error yaw: the yaw angle error, unit is degree
The meaning of each col in the table
mean: evaluation value of the error
std: the standard deviation of the error
max: the maximum value of the error
< xx: percentage of frames whose error is smaller than the indicated range
con_frame(): the maximum number of consecutive frames that satisfy the conditions in parentheses