You're reading the documentation for an older, but still supported, version of ROS 2. For information on the latest version, please have a look at Galactic.
Introduction to tf2
Goal: Run a turtlesim demo and see some of the power of tf2 in a multi-robot example using turtlesim.
Tutorial level: Intermediate
Time: 10 minutes
Contents
Installing the demo
Let’s start by installing the demo package and its dependencies.
sudo apt-get install ros-foxy-turtle-tf2-py ros-foxy-tf2-tools ros-foxy-tf-transformations
# Clone and build the geometry_tutorials repo using the branch that matches your installation
git clone https://github.com/ros/geometry_tutorials.git -b ros2
Additionally, install a transforms3d Python package, which provides the quaternion and euler angle transformation functionality for the tf_transformations package.
pip3 install transforms3d
Running the demo
Now that we’ve installed the turtle_tf2_py tutorial package let’s run the demo.
First, open a new terminal and source your ROS 2 installation so that ros2 commands will work.
Then run the following command:
ros2 launch turtle_tf2_py turtle_tf2_demo.launch.py
You will see the turtlesim start with two turtles.

In the second terminal window type the following command:
ros2 run turtlesim turtle_teleop_key
Once the turtlesim is started you can drive the central turtle around in the turtlesim using the keyboard arrow keys, select the second terminal window so that your keystrokes will be captured to drive the turtle.
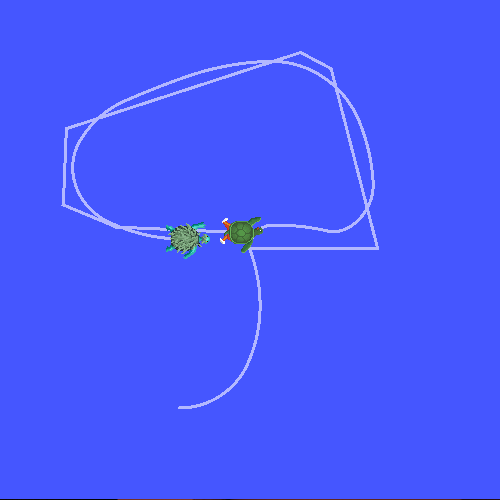

You can see that one turtle continuously moves to follow the turtle you are driving around.
What is happening?
This demo is using the tf2 library to create three coordinate frames: a world frame, a turtle1 frame, and a turtle2 frame.
This tutorial uses a tf2 broadcaster to publish the turtle coordinate frames and a tf2 listener to compute the difference in the turtle frames and move one turtle to follow the other.
tf2 tools
Now let’s look at how tf2 is being used to create this demo.
We can use tf2_tools to look at what tf2 is doing behind the scenes.
1 Using view_frames
view_frames creates a diagram of the frames being broadcasted by tf2 over ROS.
ros2 run tf2_tools view_frames.py
You will see:
Listening to tf data during 5 seconds...
Generating graph in frames.pdf file...
Here a tf2 listener is listening to the frames that are being broadcasted over ROS and drawing a tree of how the frames are connected.
To view the tree, open the resulting frames.pdf with your favorite PDF viewer.
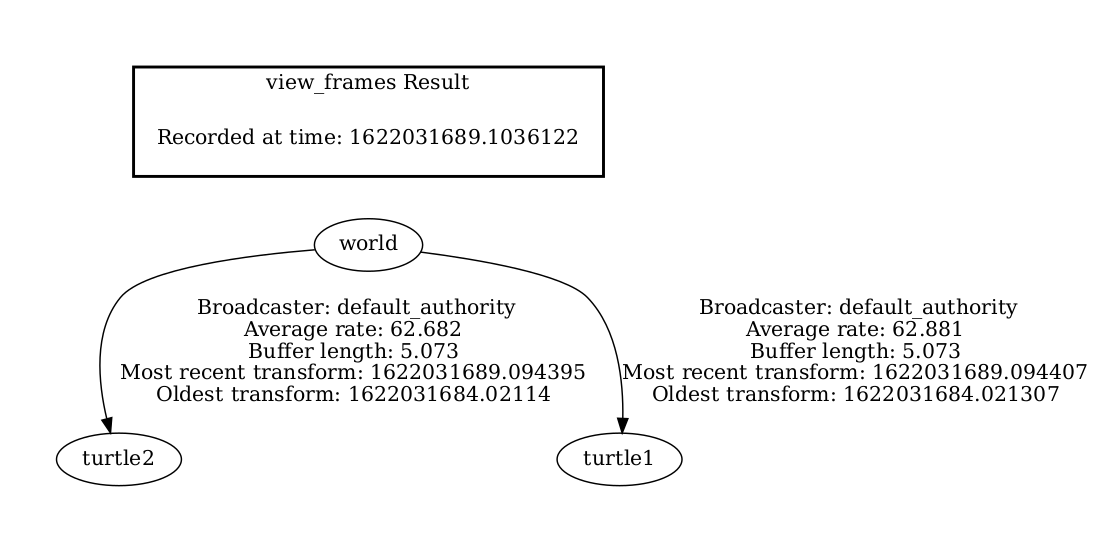
Here we can see three frames that are broadcasted by tf2: world, turtle1, and turtle2.
The world here is the parent of the turtle1 and turtle2 frames.
view_frames also report some diagnostic information about when the oldest and most
recent frame transforms were received and how fast the tf2 frame is published to tf2 for debugging purposes.
2 Using tf2_echo
tf2_echo reports the transform between any two frames broadcasted over ROS.
Usage:
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo [reference_frame] [target_frame]
Let’s look at the transform of the turtle2 frame with respect to turtle1 frame which is equivalent to:
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo turtle2 turtle1
You will see the transform displayed as the tf2_echo listener receives the frames broadcasted over ROS2.
At time 1622031731.625364060
- Translation: [2.796, 1.039, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.000, 0.000, 0.202, 0.979]
At time 1622031732.614745114
- Translation: [1.608, 0.250, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.000, 0.000, 0.032, 0.999]
As you drive your turtle around you will see the transform change as the two turtles move relative to each other.
rviz and tf2
rviz is a visualization tool that is useful for examining tf2 frames.
Let’s look at our turtle frames using rviz.
Let’s start rviz with the turtle_rviz.rviz configuration file using the -d option:
ros2 run rviz2 rviz2 -d $(ros2 pkg prefix --share turtle_tf2_py)/rviz/turtle_rviz.rviz
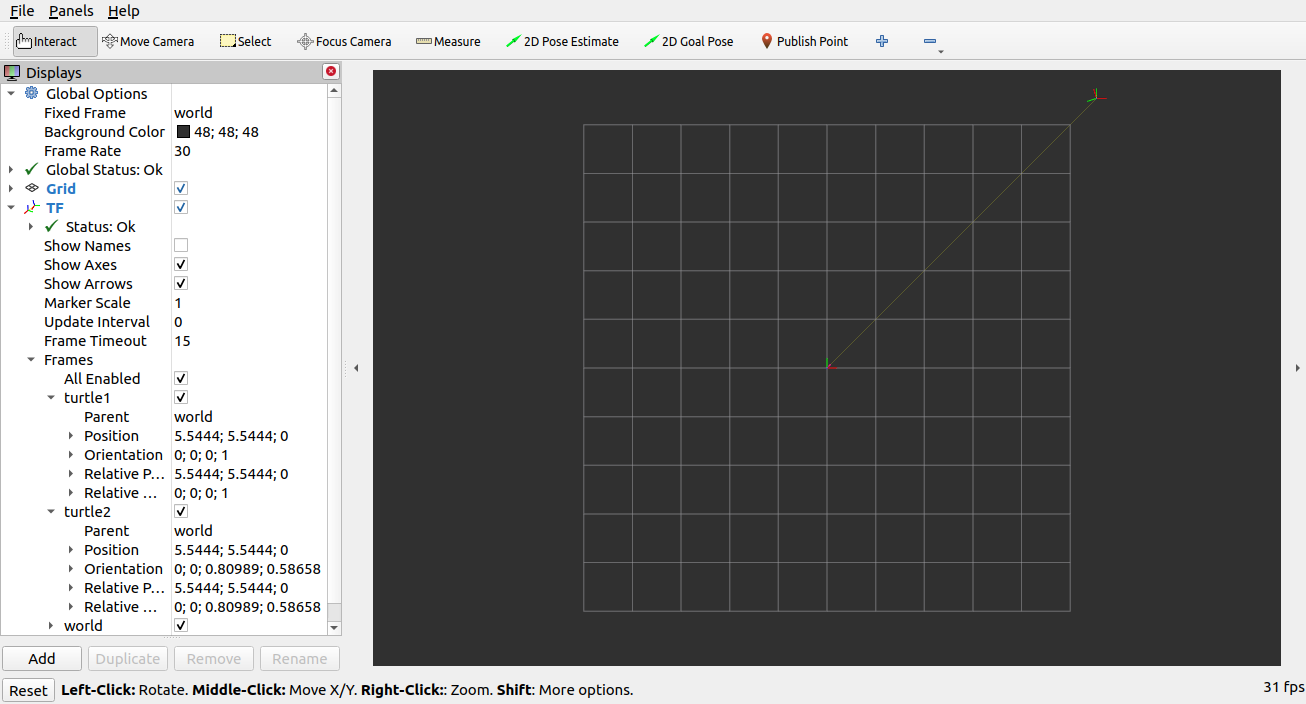
In the side bar you will see the frames broadcasted by tf2. As you drive the turtle around you will see the frames move in rviz.