Mermaid 用户指南 – 为初学者而设¶
Mermaid 由三部分组成:部署、语法和配置。
本节讲述了部署 Mermaid 的不同方法。学习 语法 对初学者会有很大帮助。
一般来说,实时编辑器足以满足美人鱼的大多数一般用途,是一个开始学习的好地方。
建议绝对的初学者查看关于实时编辑器的视频 教程,以更好地了解 mermaid。
四种使用 mermaid 的方法:¶
在 mermaid.live 中使用 Mermaid 实时编辑器。
在你熟悉的程序中使用 mermaid 插件。
调用 Mermaid Javascript API。
将 Mermaid 作为一个依赖关系进行部署。
注意:我们建议你审查所有的方法,并选择最适合你项目的方法。
更深入的信息可以在 用法 找到。
1. Using the Live Editor¶
Available at mermaid.live
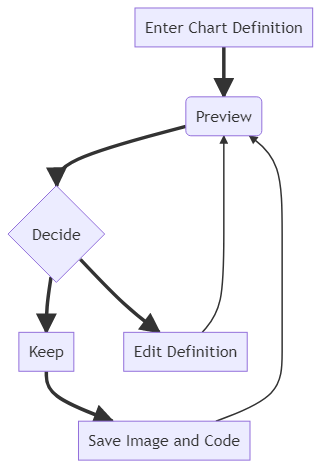
In the Code section one can write or edit raw mermaid code, and instantly Preview the rendered result on the panel beside it.
The Configuration Section is for changing the appearance and behavior of mermaid diagrams. An easy introduction to mermaid configuration is found in the Advanced usage section. A complete configuration reference cataloging the default values can be found on the mermaidAPI page.
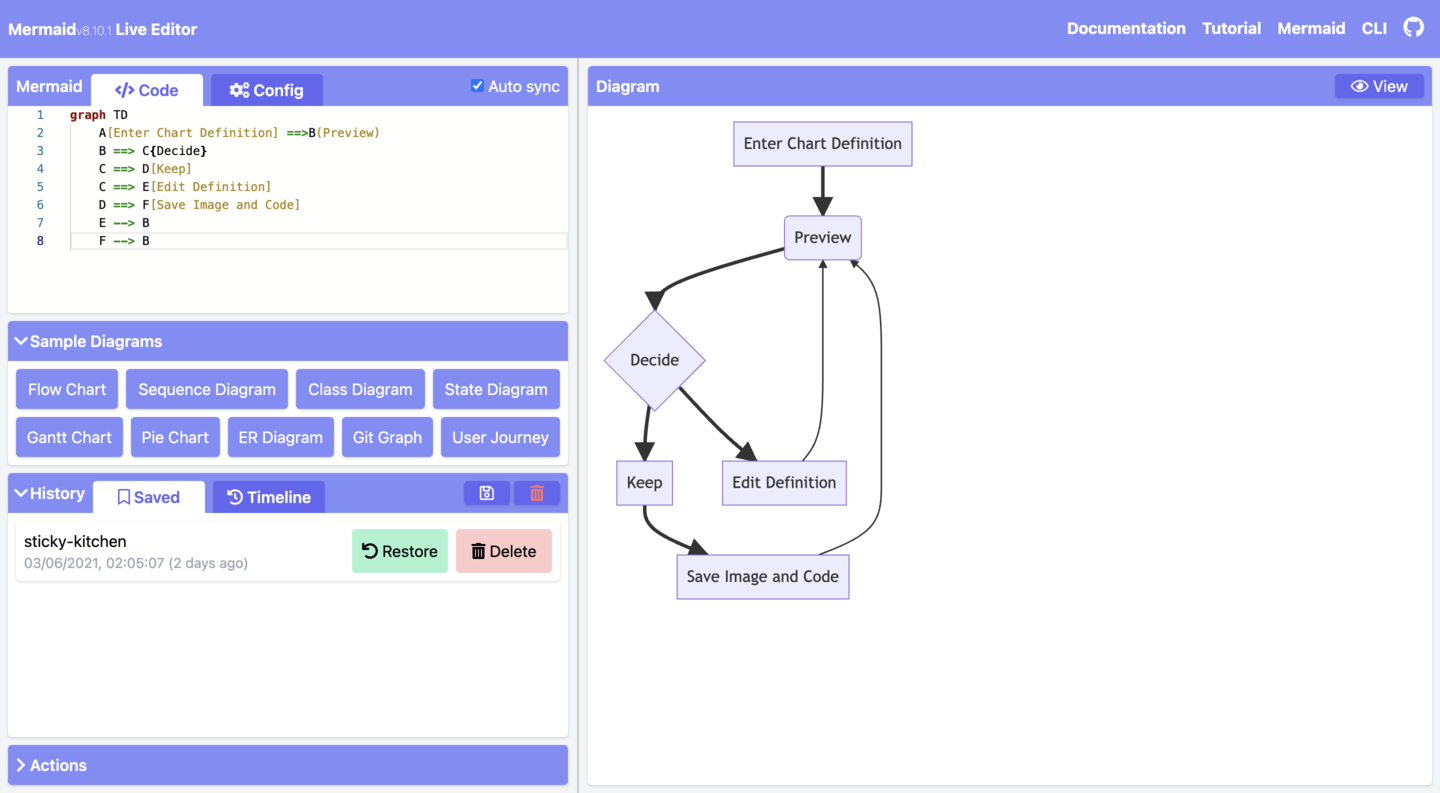
Editing History¶
Your code will be autosaved every minute into the Timeline tab of History which shows the most recent 30 items.
You can manually save code by clicking the Save icon in the History section. It can also be accessed in the Saved tab. This is stored in the browser storage only.
Saving a Diagram:¶
You may choose any of the methods below, to save it
We recommend that you save your diagram code on top of any method you choose, in order to make edits and modifications further down the line.
Editing your diagrams¶
Editing is as easy as pasting your Diagram code, into the code section of the Live Editor.
Loading from Gists¶
The Gist you create should have a code.mmd file and optionally a config.json. Example
To load a gist into the Editor, you can use https://mermaid-js.github.io/mermaid-live-editor/edit?gist=https://gist.github.com/sidharthv96/6268a23e673a533dcb198f241fd7012a
and to View, https://mermaid-js.github.io/mermaid-live-editor/view?gist=https://gist.github.com/sidharthv96/6268a23e673a533dcb198f241fd7012a
2. Using Mermaid Plugins:¶
你可以使用插件从流行的应用程序中生成 mermaid。它可以用同样的方式来完成,你会使用实时编辑器。这里有一个 mermaid 插件 的列表。
这一点在 用法部分 中有更详细的介绍。
3. Calling the Javascript API¶
This method can be used with any common web server like Apache, IIS, nginx, node express.
You will also need a text editing tool like Notepad++ to generate a .html file. It is then deployed by a web browser (such as Firefox, Chrome, Safari, but not Internet Explorer).
The API works by pulling rendering instructions from the source mermaid.js in order to render diagrams on the page.
Requirements for the Mermaid API.¶
When writing the .html file, we give three instructions inside the html code to the web browser:
a. A reference for fetching the online mermaid renderer, through the mermaid.js or mermaid.min.js.
b. The mermaid code for the diagram we want to create.
c. The mermaid.initialize() call, which dictates the appearance of diagrams and also starts the rendering process .
a. A reference to the external CDN in a <script src> tag, or a reference to mermaid.js as a separate file.:
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mermaid/dist/mermaid.min.js"></script>
</body>
b. The embedded mermaid diagram definition inside a <div class="mermaid">:
<body>
Here is a mermaid diagram:
<div class="mermaid">
graph TD A[Client] --> B[Load Balancer] B --> C[Server01] B --> D[Server02]
</div>
</body>
Notes: Every Mermaid chart/graph/diagram definition, should have separate <div> tags.
c. The mermaid.initialize() call.
mermaid.initialize() call takes all the definitions contained in all the <div class="mermaid"> tags that it finds in the html body and renders them into diagrams. Example:
<body>
<script>
mermaid.initialize({ startOnLoad: true });
</script>
</body>
Notes:
Rendering in Mermaid is initalized by mermaid.initialize() call. You can place mermaid.initialize() inside mermaid.min.js for brevity. However, doing the opposite lets you control when it starts looking for <div>tags inside the web page with mermaid.initialize(). This is useful when you think that not all <div> tags may have loaded on the execution of mermaid.min.js file.
startOnLoad is one of the parameters that can be defined by mermaid.initialize()
Parameter |
Description |
Type |
Values |
|---|---|---|---|
startOnLoad |
Toggle for Rendering upon loading |
Boolean |
true, false |
Working Examples¶
Here is a full working example of the mermaidAPI being called through the CDN:
<html>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mermaid/dist/mermaid.min.js"></script>
<script>
mermaid.initialize({ startOnLoad: true });
</script>
Here is one mermaid diagram:
<div class="mermaid">
graph TD A[Client] --> B[Load Balancer] B --> C[Server1] B --> D[Server2]
</div>
And here is another:
<div class="mermaid">
graph TD A[Client] -->|tcp_123| B(Load Balancer) B -->|tcp_456| C[Server1] B
-->|tcp_456| D[Server2]
</div>
</body>
</html>
Another Option:
In this example mermaid.js is referenced in src as a separate JavaScript file, in an example Path.
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="mermaid">
graph LR A --- B B-->C[fa:fa-ban forbidden] B-->D(fa:fa-spinner);
</div>
<div class="mermaid">
graph TD A[Client] --> B[Load Balancer] B --> C[Server1] B --> D[Server2]
</div>
<script src="The\Path\In\Your\Package\mermaid.js"></script>
<script>
mermaid.initialize({ startOnLoad: true });
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. Adding Mermaid as a dependency.¶
install node v16, which would have npm
download yarn using npm by entering the command below: npm install -g yarn
After yarn installs, enter the following command: yarn add mermaid
To add Mermaid as a Dev Dependency yarn add –dev mermaid
Comments from Knut Sveidqvist, creator of mermaid:
In early versions of mermaid, the
<script src>tag was invoked in the<head>part of the web page. Nowadays we can place it in the<body>as seen above. Older parts of the documentation frequently reflects the previous way which still works.