桥梁裂缝检测
内容
桥梁裂缝检测¶
下载数据集:
kaggle datasets download -d xinzone/surface-crack
回到根目录:
cd ../..
E:\kaggle\crack-book
获取数据集的根目录:
from apps.dataset import kaggle_root
# 获取数据根目录
root = kaggle_root() + '/datasets/xinzone/surface-crack/surface-crack.zip'
读取图片:
from zipfile import ZipFile
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
def name2bunch(namelist):
'''将 namelist 转换为 bunch'''
name_bunch = {}
for name in namelist:
ns = name.split('/')
name_type = ns[0]
if name_type == 'predict':
name_bunch.setdefault(name_type, []).append(name)
else:
label = ns[1]
name_bunch.setdefault(name_type, []).append((name, label))
return name_bunch
class ZipImage:
def __init__(self, Z):
'''
Z: 图片的 ZipFile 对象
'''
self.Z = Z
self.name_bunch = name2bunch(self.Z.namelist())
def array(self, name):
'''获取给定的 name 的图片像素信息'''
with self.Z.open(name) as fp:
with Image.open(fp) as im:
img = np.array(im)
return img
def split(self, data_type):
'''
data_type: 'test', 'train', 'valid', 'predict'
'''
for ns in self.name_bunch[data_type]:
if ns == 'predict':
img = self.array(ns)
yield img
else:
name, label = ns
img = self.array(name)
yield img, label
Z = ZipFile(root)
I = ZipImage(Z)
train = I.split('train')
test = I.split('test')
valid = I.split('valid')
predict = I.split('predict')
for img, label in train:
print(label)
break
Image.fromarray(img)
Negative

图片灰度化¶
选择一张阳性的图片:
img = I.array('train/Positive/IMG_0487_9_13.jpg')
im = Image.fromarray(img)
获取 R, G, B:
def RGB(im):
R, G, B = im.split()
R = np.array(R)
G = np.array(G)
B = np.array(B)
return R, G, B
R, G, B = RGB(im)
图像灰度化的基本原理是:在 YUV 的颜色空间中,Y 分量代表了点的亮度,该值反映的是亮度等级信息。Y 分量的计算方法如下所示:
\[
Y = 0.3 R + 0.59 G + 0.11 B
\]
def gray(im):
R, G, B = RGB(im)
Y = 0.3*R + 0.59*G + 0.11*B
Y = Y.astype('uint8') # 将浮点数转换为 uint8
return Y
im

Y = gray(im)
Image.fromarray(Y) # 灰度化的结果

波谷阈值分割¶
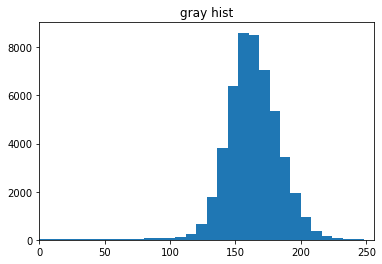
经过细心的观察训练样本 patch,我们发现,含有裂缝的正样本 patch 的灰度分布,有一个很明显的特点:正样本 patch 的灰度分布存在一个明显的全局波谷,小于此波谷灰度值的部分对应裂缝像素,大于此波谷灰度值的部分对应非裂缝像素。
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax.hist(Y.ravel(), bins=32, range=[0, 256])
ax.set_xlim(0, 256)
ax.set_title('gray hist');
Canny Edge¶
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from skimage.filters import median
from skimage.morphology import disk
from scipy import ndimage
from skimage.filters import laplace
import cv2
# def sobel_filters(img):
# Kx = np.array([[-1, 0, 1], [-2, 0, 2], [-1, 0, 1]], np.float32)
# Ky = np.array([[1, 2, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -2, -1]], np.float32)
# Ix = ndimage.filters.convolve(img, Kx)
# Iy = ndimage.filters.convolve(img, Ky)
# G = np.hypot(Ix, Iy)
# G = G / G.max() * 255
# theta = np.arctan2(Iy, Ix)
# return G, theta
def canny_edge(gray):
# noise removal
blur_img = median(gray, disk(3))
blur_img = np.array(blur_img, dtype=np.uint8)
#s = np.array(s,dtype=np.uint8)
# Image smoothing: bilateral filter
bilateral = cv2.bilateralFilter(blur_img, 5, 75, 75)
# Canny edge detection
edges = cv2.Canny(bilateral, 100, 220)
return edges
edges = canny_edge(Y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax[0].imshow(img, cmap='gray')
ax[0].set_title('origin')
ax[1].imshow(edges, cmap='gray')
ax[1].set_title('binary')
plt.show()

