4. 在Windows上使用 Python¶
本文档旨在概述在 Microsoft Windows 上使用 Python 时应了解的特定于 Windows 的行为。
与大多数UNIX系统和服务不同,Windows系统没有预安装Python。多年来CPython 团队已经编译了每一个 发行版 的Windows安装程序(MSI 包),已便Windows 用户下载和安装。这些安装程序主要用于每个用户单独安装Python时,添加核心解释器和库。安装程序还可以为一台机器的所有用户安装,并且可以为应用程序本地分发提供单独的zip文件。
如 PEP 11 所述,Python 发布版对某个 Windows 平台的支持仅限于被 Microsoft 视为处于延长支持周期内的版本。 这意味着 Python 3.12 支持 Windows 8.1 及其后的版本。 如果你需要 Windows 7 支持,请安装 Python 3.8。
Windows提供了许多不同的安装程序,每个安装程序都有一定的优点和缺点。
完整安装程序 内含所有组件,对于使用Python 进行任何类型项目的开发人员而言,它是最佳选择。
Microsoft Store包 is a simple installation of Python that is suitable for running scripts and packages, and using IDLE or other development environments. It requires Windows 10 and above, but can be safely installed without corrupting other programs. It also provides many convenient commands for launching Python and its tools.
nuget.org 安装包 是用于持续集成系统的轻量级安装。它可用于构建Python包或运行脚本,但不可更新且没有用户界面工具。
可嵌入的包 是Python的最小安装包,适合嵌入到更大的应用程序中。
4.1. 完整安装程序¶
4.1.1. 安装步骤¶
四个 Python 3.12 安装程序可供下载 - 32位和64位版本的各有两个。 web installer (网络安装包)是一个小的初始化工具,它将在安装过程中,根据需要自动下载所需的组件。 offline installer (离线安装包)内含默认安装所需的组件,可选择功能仍需要Internet连接下载。请参阅 免下载安装 以了解在安装过程中避免下载的其他方法。
启动安装程序后,可以选择以下两个选项之一:
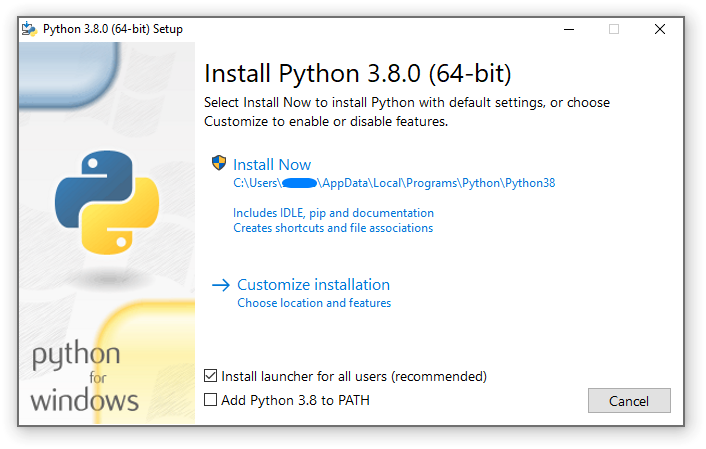
如果选择“Install Now(立即安装)”:
您 不 需要成为管理员(除非需要对C运行库进行系统更新,或者为所有用户安装 适用于Windows的Python启动器 )
Python将安装到您的用户目录中
适用于Windows的Python启动器 将根据第一页底部的选项安装
将安装标准库,测试套件,启动器和pip
如果选择将安装目录将添加到
PATH快捷方式仅对当前用户可见
选择“自定义安装”将允许您选择:要安装的功能、安装位置、其他选项或安装后的操作。如果要安装调试符号或二进制文件,您需要使用此选项。
如要为全部用户安装,应选择“自定义安装”。在这种情况下:
您可能需要提供管理凭据或批准
Python 将安装到Program Files目录中
适用于Windows的Python启动器 将安装到Windows目录中
安装期间可以选择可选功能
标准库可以预编译为字节码
如果选中,安装目录将添加到系统
PATH快捷方式所有用户可用
4.1.2. 删除 MAX_PATH 限制¶
历史上Windows的路径长度限制为260个字符。这意味着长于此的路径将无法解决并导致错误。
在最新版本的 Windows 中,此限制可被扩展到大约 32,000 个字符。 但需要让管理员激活“启用 Win32 长路径”组策略,或在注册表键 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem 中设置 LongPathsEnabled 为 1。
这允许 open() 函数,os 模块和大多数其他路径功能接受并返回长度超过 260 个字符的路径。
更改上述选项后,无需进一步配置。
在 3.6 版更改: Python中启用了对长路径的支持。
4.1.3. 无UI 安装¶
安装程序UI中的所有选项也可以从命令行指定,允许脚本安装程序在许多机器上复制安装,而无需用户交互。还可以在不禁用UI的情况下设置这些选项,以更改一些默认值。
The following options (found by executing the installer with /?) can be
passed into the installer:
名称 |
描述 |
|---|---|
/passive |
to display progress without requiring user interaction |
/quiet |
to install/uninstall without displaying any UI |
/simple |
to prevent user customization |
/uninstall |
to remove Python (without confirmation) |
/layout [directory] |
to pre-download all components |
/log [filename] |
to specify log files location |
所有其他选项都传递为 name=value ,其中值通常是 0 来禁用某个特性, 1 来启用某个特性或路径。可用选项的完整列表如下所示。
名称 |
描述 |
默认值 |
|---|---|---|
InstallAllUsers |
为所有用户安装。 |
0 |
TargetDir |
安装目录 |
基于InstallAllUsers选择 |
DefaultAllUsersTargetDir |
为所有用户安装时的默认安装路径 |
|
DefaultJustForMeTargetDir |
仅为当前用户安装时的默认安装路径 |
|
DefaultCustomTargetDir |
UI中显示的默认自定义安装目录 |
(空) |
AssociateFiles |
如果还安装了启动器,则创建文件关联。 |
1 |
CompileAll |
将所有 |
0 |
PrependPath |
Prepend install and Scripts
directories to |
0 |
AppendPath |
Append install and Scripts
directories to |
0 |
Shortcuts |
如果已安装,为解释器,文档和IDLE创建快捷方式 |
1 |
Include_doc |
安装Python手册 |
1 |
Include_debug |
安装调试二进制文件 |
0 |
Include_dev |
Install developer headers and libraries. Omitting this may lead to an unusable installation. |
1 |
Include_exe |
Install |
1 |
Include_launcher |
安装 适用于Windows的Python启动器 . |
1 |
InstallLauncherAllUsers |
Installs the launcher for all
users. Also requires
|
1 |
Include_lib |
Install standard library and extension modules. Omitting this may lead to an unusable installation. |
1 |
Include_pip |
安装捆绑的pip和setuptools |
1 |
Include_symbols |
Install debugging symbols ( |
0 |
Include_tcltk |
安装Tcl/Tk 支持和IDLE |
1 |
Include_test |
安装标准库测试套件 |
1 |
Include_tools |
安装实用程序脚本 |
1 |
LauncherOnly |
仅安装启动器。这将覆盖大多数其他选项。 |
0 |
SimpleInstall |
禁用大多数安装UI |
0 |
SimpleInstallDescription |
使用简化安装UI时显示的自定义消息。 |
(空) |
例如,要以静默方式全局安装默认的Python,您可以(在命令提示符>)使用以下命令:
python-3.9.0.exe /quiet InstallAllUsers=1 PrependPath=1 Include_test=0
要允许用户在没有测试套件的情况下轻松安装Python的个人副本,可以使用以下命令提供快捷方式。这将显示一个简化的初始页面,不允许自定义:
python-3.9.0.exe InstallAllUsers=0 Include_launcher=0 Include_test=0
SimpleInstall=1 SimpleInstallDescription="Just for me, no test suite."
(请注意,省略启动器也会省略文件关联,并且仅在全局安装包含启动器时才建议用于每用户安装。)
上面列出的选项也可以在一个名为 unattend.xml 的文件中与可执行文件一起提供。此文件指定选项和值的列表。作为属性提供的值,(如果可能)它将转换为数字。作为文本提供的值,始终保留为字符串。此示例文件设置与上一示例采用相同的选项:
<Options>
<Option Name="InstallAllUsers" Value="no" />
<Option Name="Include_launcher" Value="0" />
<Option Name="Include_test" Value="no" />
<Option Name="SimpleInstall" Value="yes" />
<Option Name="SimpleInstallDescription">Just for me, no test suite</Option>
</Options>
4.1.4. 免下载安装¶
由于下载的初始安装包中未包含Python的某些可选功能,如果选择安装这些功能可能需要Internet连接。为了避免这种需要,可以按需下载所有可能的组件,以创建一个完整的布局,该布局将不再需要internet连接,而不管所选择的特性是什么。请注意,此下载可能比要求的要大,但是如果要执行大量安装,则拥有本地缓存的副本非常有用。
从命令提示符执行以下命令以下载所有可能的必需文件。 请记得要将 python-3.9.0.exe 替换为安装程序的实际名称,并在单独的目录中创建子目录以避免同名文件间的冲突。
python-3.9.0.exe /layout [optional target directory]
您也可以指定 /quiet 选项来隐藏进度显示。
4.1.5. 修改安装¶
安装Python后,您可以通过Windows中的“程序和功能”工具添加或删除功能。选择Python条目并选择“卸载/更改”以在维护模式下打开安装程序。
“修改” 允许您通过修改复选框来添加或删除功能 - 未更改的复选框将不会安装或删除任何内容。在此模式下无法更改某些选项,例如安装目录;要修改这些,您需要完全删除然后重新安装Python。
“修复” 将使用当前设置验证应安装的所有文件,并替换已删除或修改的任何文件
“卸载” 将完全删除Python,但 适用于Windows的Python启动器 除外,它在“程序和功能”中有自己的条目。
4.2. Microsoft Store包¶
3.7.2 新版功能.
Microsoft Store包是一个易于安装的Python解释器,主要用于交互式使用,例如,学生。
要安装软件包,请确保您拥有最新的Windows 10更新,并在Microsoft Store应用程序中搜索 “Python 3.12” 。确保您选择的应用程序由 Python Software Foundation 发布并安装。
警告
Python将始终在Microsoft Store上免费提供。如果要求您付款,则表示您没有选择正确的包。
安装完成后,可以在开始菜单中找到它来启动 Python。或者可以在命令提示符或 PowerShell 会话中输入 python 来启动。此外可以输入 pip 或 idle 来使用 pip 和 IDLE。IDLE 也在开始菜单中。
所有这三个命令也可以使用版本号后缀,例如, python3.exe 和 python3.x.exe 以及 python.exe (其中 3.x 是您要启动的特定版本,例如 3.12 )。在 设置-->主页-->应用和功能 页面中,点选 管理可选功能 ,选择与每个命令关联的python版本。建议确保 pip 和 idle 与选择的 python 版本一致。
可以使用 python -m venv 创建虚拟环境并激活并正常使用。
如果你已经安装了另一个版本的Python并将它添加到你的 PATH 变量中,那么它将作为 python.exe 而不是来自Microsoft Store的那个。要访问新安装,请使用 python3.exe 或 python3.x.exe 。
py.exe 启动器将检测此 Python 安装版,但会优先使用来自传统安装器的安装版。
要删除Python,请打开“设置”并使用“应用程序和功能”,或者在“开始”中找到Python,然后右键单击以选择“卸载”。卸载将删除该已安装Python程序中的所有软件包,但不会删除任何虚拟环境
4.2.1. Known issues¶
4.2.1.1. Redirection of local data, registry, and temporary paths¶
Because of restrictions on Microsoft Store apps, Python scripts may not have
full write access to shared locations such as TEMP and the registry.
Instead, it will write to a private copy. If your scripts must modify the
shared locations, you will need to install the full installer.
At runtime, Python will use a private copy of well-known Windows folders and the registry.
For example, if the environment variable %APPDATA% is c:\Users\<user>\AppData\,
then when writing to C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local will write to
C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.8_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\Local\.
When reading files, Windows will return the file from the private folder, or if that does not exist, the
real Windows directory. For example reading C:\Windows\System32 returns the contents of C:\Windows\System32
plus the contents of C:\Program Files\WindowsApps\package_name\VFS\SystemX86.
You can find the real path of any existing file using os.path.realpath():
>>> import os
>>> test_file = 'C:\\Users\\example\\AppData\\Local\\test.txt'
>>> os.path.realpath(test_file)
'C:\\Users\\example\\AppData\\Local\\Packages\\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.8_qbz5n2kfra8p0\\LocalCache\\Local\\test.txt'
When writing to the Windows Registry, the following behaviors exist:
Reading from
HKLM\\Softwareis allowed and results are merged with theregistry.datfile in the package.Writing to
HKLM\\Softwareis not allowed if the corresponding key/value exists, i.e. modifying existing keys.Writing to
HKLM\\Softwareis allowed as long as a corresponding key/value does not exist in the package and the user has the correct access permissions.
有关此限制的技术原理的更多细节,请查询 Microsoft 已打包完全可信应用的文档,当前位于 docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/msix/desktop/desktop-to-uwp-behind-the-scenes
4.3. nuget.org 安装包¶
3.5.2 新版功能.
nuget.org是一个精简的Python环境,用于在没有全局安装Python的系统的持续集成和构建。虽然Nuget是“.NET的包管理器”,但是对于包含构建时工具的包来说,它也可以很好地工作。
访问 nuget.org 获取有关使用nuget的最新信息。下面的摘要对Python开发人员来说已经足够了。
nuget.exe 命令行工具可以直接从 https://aka.ms/nugetclidl 下载,例如,使用curl或PowerShell。使用该工具安装64位或32位最新版本的Python:
nuget.exe install python -ExcludeVersion -OutputDirectory .
nuget.exe install pythonx86 -ExcludeVersion -OutputDirectory .
To select a particular version, add a -Version 3.x.y. The output directory
may be changed from ., and the package will be installed into a
subdirectory. By default, the subdirectory is named the same as the package,
and without the -ExcludeVersion option this name will include the specific
version installed. Inside the subdirectory is a tools directory that
contains the Python installation:
# Without -ExcludeVersion
> .\python.3.5.2\tools\python.exe -V
Python 3.5.2
# With -ExcludeVersion
> .\python\tools\python.exe -V
Python 3.5.2
通常,nuget包不可升级,应该平行安装较新版本并使用完整路径引用。或者,手动删除程序包目录并再次安装。如果在构建之间不保留文件,许多CI系统将自动执行此操作。
除了 tools 目录外,还有一个 build\native 目录。它包含一个MSBuild属性文件 python.props ,可以在C++项目中使用该文件来引用Python安装。包含这些设置将自动在生成中使用标头和导入库。
nuget.org上的包信息页是 www.nuget.org/packages/python 对于64位版本和 www.nuget.org/packages/pythonx86 表示32位版本。
4.4. 可嵌入的包¶
3.5 新版功能.
嵌入式发行版是一个包含最小Python环境的ZIP文件。它旨在作为另一个应用程序的一部分,而不是由最终用户直接访问。
解压缩后,嵌入式发行版(几乎)与用户系统完全隔离,包括环境变量、系统注册表设置和已安装的软件包。标准库作为预先编译和优化的 .pyc 文件包含在ZIP中,并提供了 python3.dll , python37.dll , python.exe 和 pythonw.exe 文件。不包括Tcl/tk(包括所有依赖项,如Idle),pip和Python文档。
备注
The embedded distribution does not include the Microsoft C Runtime and it is
the responsibility of the application installer to provide this. The
runtime may have already been installed on a user’s system previously or
automatically via Windows Update, and can be detected by finding
ucrtbase.dll in the system directory.
第三方软件包应该由应用程序与嵌入式发行版一起安装。这个发行版不支持像常规Python安装那样使用pip来管理依赖关系,不过可以小心地将pip包含进来并使用它进行自动更新。通常,第三方包应该作为应用程序的一部分(“打包”)处理,以便开发人员在向用户提供更新之前能够确保与新版本兼容。
下面描述了这个发行版的两个推荐用例。
4.4.1. Python应用程序¶
用Python编写的应用程序并不一定要求用户了解这一事实。在这种情况下,可以使用嵌入式发行版在安装包中包含Python的私有版本。根据它应该有多透明(或者相反,它应该看起来有多专业),有两个选项。
使用专门的可执行文件作为启动程序需要一些编码,但为用户提供了最透明的体验。使用定制的启动器,没有明显的迹象表明程序是在Python上运行的:图标可以定制,公司和版本信息可以指定,文件关联可以正常运行。在大多数情况下,自定义启动程序应该只需使用硬编码的命令行就能调用 Py_Main
更简单的方法是提供批处理文件或生成的快捷方式,使用所需的命令行参数直接调用 python.exe 或 pythonw.exe 。在这种情况下,应用程序将显示为Python而不是其实际名称,并且用户可能无法将其与其他正在运行的Python进程或文件关联区分开来。
对于后一种方法,包应该与Python可执行文件一起作为目录安装,以确保它们在路径上可用。使用专用的启动器,包可以位于其他位置,因为在启动应用程序之前有机会指定搜索路径。
4.4.2. 嵌入Python¶
用本地代码编写的应用程序通常需要某种形式的脚本语言,嵌入式Python发行版可以用于此目的。通常,应用程序的大部分都是本机代码,某些部分将调用 python.exe 或直接使用 python3.dll 。无论是哪种情况,将嵌入的发行版解压缩到应用程序安装的子目录中就足以提供可加载的Python解释器。
与应用程序使用一样,包可以安装到任何位置,因为在初始化解释器之前有机会指定搜索路径。否则,使用嵌入式发行版和常规安装之间没有根本区别。
4.5. 替代捆绑包¶
除了标准的CPython发行版之外,还有一些包含附加功能的修改包。以下是热门版本及其主要功能的列表:
- ActivePython
具有多平台兼容性的安装程序,文档,PyWin32
- Anaconda
流行的科学模块(如numpy,scipy和pandas)和
conda包管理器。- Enthought Deployment Manager
“The Next Generation Python Environment and Package Manager”.
Previously Enthought provided Canopy, but it reached end of life in 2016.
- WinPython
特定于Windows的发行版,包含用于构建包的预构建科学包和工具。
请注意,这些软件包可能不包含最新版本的Python或其他库,并且不由核心Python团队维护或支持。
4.6. 配置Python¶
要从命令提示符方便地运行Python,您可以考虑在Windows中更改一些默认环境变量。虽然安装程序提供了为您配置PATH和PATHEXT变量的选项,但这仅适用于单版本、全局安装。如果您经常使用多个版本的Python,请考虑使用 适用于Windows的Python启动器 。
4.6.1. 附录:设置环境变量¶
Windows允许在用户级别和系统级别永久配置环境变量,或临时在命令提示符中配置环境变量。
要临时设置环境变量,请打开命令提示符并使用 set 命令:
C:\>set PATH=C:\Program Files\Python 3.9;%PATH%
C:\>set PYTHONPATH=%PYTHONPATH%;C:\My_python_lib
C:\>python
这些环境变量的更改将应用于在该控制台中执行的任何其他命令,并且,由该控制台启动的任何应用程序都继承设这些设置。
在百分号中包含的变量名将被现有值替换,允许在开始或结束时添加新值。通过将包含 python.exe 的目录添加到开头来修改 PATH 是确保启动正确版本的Python的常用方法。
要永久修改默认环境变量,请单击“开始”并搜索“编辑环境变量”,或打开系统属性的 高级系统设置 ,然后单击 环境变量 按钮。在此对话框中,您可以添加或修改用户和系统变量。要更改系统变量,您需要对计算机进行无限制访问(即管理员权限)。
备注
Windows会将用户变量串联在系统变量 之后 ,这可能会在修改 PATH 时导致意外结果。
The PYTHONPATH variable is used by all versions of Python,
so you should not permanently configure it unless the listed paths
only include code that is compatible with all of your installed Python
versions.
参见
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/procthread/environment-variables
Overview of environment variables on Windows
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/set_1
The
setcommand, for temporarily modifying environment variables- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/setx
The
setxcommand, for permanently modifying environment variables
4.6.2. 查找Python可执行文件¶
在 3.5 版更改.
除了使用自动创建的Python解释器的开始菜单项之外,您可能还想在命令提示符下启动Python。安装程序有一个选项可以为您设置。
在安装程序的第一页上,可以选择标记为“将Python添加到环境变量”的选项,以使安装程序将安装位置添加到 PATH 。还添加了 Scripts\ 文件夹的位置。这允许你输入 python 来运行解释器,并且 pip 用于包安装程序。因此,您还可以使用命令行选项执行脚本,请参阅 命令行 文档。
如果在安装时未启用此选项,则始终可以重新运行安装程序,选择“修改”并启用它。或者,您可以使用 附录:设置环境变量 的方法手动修改 PATH 。您需要将Python安装目录添加到 PATH 环境变量中,该内容与其他条目用分号分隔。示例变量可能如下所示(假设前两个条目已经存在):
C:\WINDOWS\system32;C:\WINDOWS;C:\Program Files\Python 3.9
4.7. UTF-8 模式¶
3.7 新版功能.
Windows still uses legacy encodings for the system encoding (the ANSI Code
Page). Python uses it for the default encoding of text files (e.g.
locale.getencoding()).
这可能会造成问题,因为因特网和大多数 Unix 系统包括 WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) 广泛使用 UTF-8。
你可以使用 Python UTF-8 模式 将默认的文本编码格式改为 UTF-8。 要启用 Python UTF-8 模式 可以通过 -X utf8 命令行选项,或者 PYTHONUTF8=1 环境变量。 请参阅 PYTHONUTF8 了解如何启用 UTF-8 模式,并参阅 附录:设置环境变量 了解如何修改环境变量。
当 Python UTF-8 模式 启用时,你仍然可以通过 “mbcs” 编解码器使用系统编码格式(ANSI 代码页)。
请注意添加 PYTHONUTF8=1 到默认环境变量将会影响你的系统中的所有 Python 3.7+ 应用。 如果你有任何 Python 3.7+ 应用仍然依赖于传统的系统编码格式,则推荐设置临时环境变量或使用 -X utf8 命令行选项。
4.8. 适用于Windows的Python启动器¶
3.3 新版功能.
用于Windows的Python启动器是一个实用程序,可帮助定位和执行不同的Python版本。它允许脚本(或命令行)指示特定Python版本的首选项,并将定位并执行该版本。
与 PATH 变量不同,启动器将正确选择最合适的Python版本。它更倾向于按用户安装而不是系统安装,并按语言版本排序,而不是使用最新安装的版本。
启动器最初是在 PEP 397 中指定的。
4.8.1. 入门¶
4.8.1.1. 从命令行¶
在 3.6 版更改.
System-wide installations of Python 3.3 and later will put the launcher on your
PATH. The launcher is compatible with all available versions of
Python, so it does not matter which version is installed. To check that the
launcher is available, execute the following command in Command Prompt:
py
您应该会发现已安装的最新版本的Python已启动 - 它可以正常退出,并且将指定的任何其他命令行参数直接发送到Python。
If you have multiple versions of Python installed (e.g., 3.7 and 3.12) you will have noticed that Python 3.12 was started - to launch Python 3.7, try the command:
py -3.7
If you want the latest version of Python 2 you have installed, try the command:
py -2
You should find the latest version of Python 3.x starts.
If you see the following error, you do not have the launcher installed:
'py' is not recognized as an internal or external command,
operable program or batch file.
除非在安装时选择了该选项,单个用户安装的Python不会将启动程序添加到 PATH 。
The command:
py --list
displays the currently installed version(s) of Python.
4.8.1.2. 从虚拟环境¶
3.5 新版功能.
如果启动程序运行时没有明确的Python版本,并且虚拟环境(使用标准库创建 venv 模块或外部 virtualenv 工具)处于活动状态,则启动程序将运行虚拟环境的解释器而不是全局的。要运行全局解释器,请停用虚拟环境,或显式指定全局Python版本。
4.8.1.3. 从脚本¶
让我们创建一个测试Python脚本 - 创建一个名为``hello.py``的文件,其中包含以下内容
#! python
import sys
sys.stdout.write("hello from Python %s\n" % (sys.version,))
From the directory in which hello.py lives, execute the command:
py hello.py
您应该注意到最新的Python 2.x安装的版本号已打印出来。现在尝试将第一行更改为:
#! python3
Re-executing the command should now print the latest Python 3.x information.
As with the above command-line examples, you can specify a more explicit
version qualifier. Assuming you have Python 3.7 installed, try changing
the first line to #! python3.7 and you should find the 3.12
version information printed.
请注意,与交互式使用不同,裸“python”将使用您已安装的Python 2.x的最新版本。这是为了向后兼容及兼容Unix,其中命令 python 通常是指Python 2。
4.8.1.4. 从文件关联¶
安装时应该将启动器与Python文件(即 .py, .pyw, .pyc 文件)相关联。这意味着当您从Windows资源管理器中双击其中一个文件时,将使用启动程序,因此您可以使用上述相同的工具让脚本指定应使用的版本。
这样做的主要好处是,单个启动程序可以同时支持多个Python版本,具体取决于第一行的内容。
4.8.2. Shebang Lines¶
如果脚本文件的第一行以 #! 开头,则称为 “shebang” 行。Linux和其他类Unix操作系统都有对这些行的本机支持,它们通常在此类系统上用来指示应该如何执行脚本。这个启动器允许在Windows上对Python脚本使用相同的工具,上面的示例演示了它们的使用。
为了允许Python脚本中的shebang行在Unix和Windows之间移植,该启动器支持许多“虚拟”命令来指定要使用的解释器。支持的虚拟命令是:
/usr/bin/env python/usr/bin/python/usr/local/bin/pythonpython
例如,如果脚本开始的第一行
#! /usr/bin/python
将找到并使用默认的Python。因为在Unix上编写的许多Python脚本已经有了这一行,你应该发现这些脚本可以由启动器使用而无需修改。如果您在Windows上编写一个新脚本,希望在Unix上有用,那么您应该使用以 /usr 开头的一个shebang行。
Any of the above virtual commands can be suffixed with an explicit version
(either just the major version, or the major and minor version).
Furthermore the 32-bit version can be requested by adding “-32” after the
minor version. I.e. /usr/bin/python3.7-32 will request usage of the
32-bit python 3.7.
3.7 新版功能: 从python启动程序3.7开始,可以通过“-64”后缀调用64位版本。此外,可以指定没有次要的主要和架构(即 /usr/bin/python3-64 )。
在 3.11 版更改: The “-64” suffix is deprecated, and now implies “any architecture that is
not provably i386/32-bit”. To request a specific environment, use the new
-V:<TAG> argument with the complete tag.
The /usr/bin/env form of shebang line has one further special property.
Before looking for installed Python interpreters, this form will search the
executable PATH for a Python executable. This corresponds to the
behaviour of the Unix env program, which performs a PATH search.
If an executable matching the first argument after the env command cannot
be found, it will be handled as described below. Additionally, the environment
variable PYLAUNCHER_NO_SEARCH_PATH may be set (to any value) to skip
this additional search.
4.8.3. shebang lines 的参数¶
shebang lines 还可以指定要传递给Python解释器的其他选项。例如,如果你有一个shebang lines :
#! /usr/bin/python -v
然后Python将以 -v 选项启动
4.8.4. 自定义¶
4.8.4.1. 通过INI文件自定义¶
启动程序将搜索两个.ini文件 - 在当前用户的 “application data” 目录中搜索 py.ini (即通过使用 CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA 调用Windows函数 SHGetFolderPath 返回的目录)以及与启动器位于同一目录中的 py.ini 。相同的.ini文件既用于启动器的“控制台”版本(即 py.exe),也用于“windows”版本(即pyw.exe)
“应用程序目录”中指定的自定义优先于可执行文件旁边.ini文件的自定义,因此对启动程序旁边的.ini文件不具有写访问权限的用户可以覆盖该全局.ini文件中的命令。
4.8.4.2. 自定义默认的Python版本¶
在某些情况下,可以在命令中包含版本限定符,以指定命令将使用哪个Python版本。版本限定符以主版本号开头,可以选择后跟 (‘.’) 和次版本说明符。此外,可以通过添加 “-32” 或 “-64” 来指定是请求32位还是64位实现。
例如,一个shebang line 的 #!python 行没有版本限定符,而 #!python3 有一个版本限定符,它只指定一个主要版本。
如果在命令中找不到版本限定符,则可以设置环境变量 PY_PYTHON 以指定默认版本限定符。 如果未设置,则默认为 “3”。 该变量可以指定能通过命令行传递的任何值,比如 “3”, “3.7”, “3.7-32” 或 “3.7-64”。 (请注意 “-64” 选项仅适用于 Python 3.7 或更高版本中包含的启动器。)
如果没有找到次要版本限定符,则可以设置环境变量 PY_PYTHON{major} (其中 {major} 是上面确定的当前主要版本限定符)以指定完整版本。如果没有找到这样的选项,启动器将枚举已安装的Python版本并使用为主要版本找到的最新次要版本,尽管不能保证,但该版本可能是该系列中最新安装的版本。
在安装了相同(major.minor)Python版本的32位和64位的64位Windows上,64位版本将始终是首选。对于启动程序的32位和64位实现都是如此 – 这对于启动程序32位和64位都是正确的 – 如果可用,32位启动程序将倾向于执行指定版本的64位Python安装。这样就可以预测启动器的行为,只知道PC上安装了哪些版本,而不考虑它们的安装顺序(即,不知道32位或64位版本的Python和相应的启动器是否是最后安装)。如上所述,可以在版本说明符上使用可选的“-32”或“-64”后缀来更改此行为。
示例:
如果没有设置相关选项,命令
python和python2将使用安装的最新Python 2.x版本,命令python3将使用最新安装的Python 3.x.The command
python3.7will not consult any options at all as the versions are fully specified.如果
PY_PYTHON=3,命令``python`` 和python3都将使用最新安装的Python 3版本。If
PY_PYTHON=3.7-32, the commandpythonwill use the 32-bit implementation of 3.7 whereas the commandpython3will use the latest installed Python (PY_PYTHON was not considered at all as a major version was specified.)If
PY_PYTHON=3andPY_PYTHON3=3.7, the commandspythonandpython3will both use specifically 3.7
除环境变量外,还可以在启动程序使用的.INI文件中配置相同的设置。 INI文件中的部分称为 [defaults] ,键名称将与没有前导 PY_ 前缀的环境变量相同(并注意INI文件中的键名不区分大小写) 。)环境变量的内容将覆盖INI文件中指定的内容。
例如:
Setting
PY_PYTHON=3.7is equivalent to the INI file containing:
[defaults]
python=3.7
Setting
PY_PYTHON=3andPY_PYTHON3=3.7is equivalent to the INI file containing:
[defaults]
python=3
python3=3.7
4.8.5. 诊断¶
If an environment variable PYLAUNCHER_DEBUG is set (to any value), the
launcher will print diagnostic information to stderr (i.e. to the console).
While this information manages to be simultaneously verbose and terse, it
should allow you to see what versions of Python were located, why a
particular version was chosen and the exact command-line used to execute the
target Python. It is primarily intended for testing and debugging.
4.8.6. Dry Run¶
If an environment variable PYLAUNCHER_DRYRUN is set (to any value),
the launcher will output the command it would have run, but will not actually
launch Python. This may be useful for tools that want to use the launcher to
detect and then launch Python directly. Note that the command written to
standard output is always encoded using UTF-8, and may not render correctly in
the console.
4.8.7. Install on demand¶
If an environment variable PYLAUNCHER_ALLOW_INSTALL is set (to any
value), and the requested Python version is not installed but is available on
the Microsoft Store, the launcher will attempt to install it. This may require
user interaction to complete, and you may need to run the command again.
An additional PYLAUNCHER_ALWAYS_INSTALL variable causes the launcher
to always try to install Python, even if it is detected. This is mainly intended
for testing (and should be used with PYLAUNCHER_DRYRUN).
4.8.8. Return codes¶
The following exit codes may be returned by the Python launcher. Unfortunately, there is no way to distinguish these from the exit code of Python itself.
The names of codes are as used in the sources, and are only for reference. There is no way to access or resolve them apart from reading this page. Entries are listed in alphabetical order of names.
名称 |
Value |
描述 |
|---|---|---|
RC_BAD_VENV_CFG |
107 |
A |
RC_CREATE_PROCESS |
101 |
Failed to launch Python. |
RC_INSTALLING |
111 |
An install was started, but the command will need to be re-run after it completes. |
RC_INTERNAL_ERROR |
109 |
Unexpected error. Please report a bug. |
RC_NO_COMMANDLINE |
108 |
Unable to obtain command line from the operating system. |
RC_NO_PYTHON |
103 |
Unable to locate the requested version. |
RC_NO_VENV_CFG |
106 |
A |
4.9. 查找模块¶
These notes supplement the description at The initialization of the sys.path module search path with detailed Windows notes.
当找不到 ._pth 文件时, sys.path 是如何在Windows上填充的:
在开始时,添加一个空条目,该条目对应于当前目录。
如果环境变量
PYTHONPATH存在,如 环境变量 中所述,则接下来添加其条目。请注意,在Windows上,此变量中的路径必须用分号分隔,以区别于驱动器标识符中使用的冒号(C:\等)。额外的 “应用程序路径” 可以作为子键被同时添加到注册表
HKEY_CURRENT_USER和HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE分支下的\SOFTWARE\Python\PythonCore{version}\PythonPath中。 以分号分隔的路径字符串作为默认值的子键将导致每个路径都被添加到sys.path中。 (请注意所有已知的安装程序都只使用 HKLM,因此 HKCU 通常为空。)如果设置了环境变量
PYTHONHOME,则将其假定为 “Python 主目录” 。否则,主Python可执行文件的路径用于定位 “landmark 文件” (Lib\os.py或pythonXY.zip)以推断 ”Python 主目录“ 。如果找到了Python主目录,则基于该文件夹将相关的子目录添加到sys.path(Lib,plat-win等)。否则,核心Python路径是从存储在注册表中的PythonPath构造的。如果找不到Python Home,也没有指定
PYTHONPATH环境变量,并且找不到注册表项,则使用具有相对条目的默认路径(例如.\Lib; .\plat-win等等)。
如果在主可执行文件旁边或在可执行文件上一级的目录中找到 pyvenv.cfg 文件,则以下变体适用:
如果
home是一个绝对路径,并且PYTHONHOME未设置,则在推断起始位置时使用此路径而不是主可执行文件的路径。
这一切的最终结果是:
运行
python.exe,或主Python目录中的任何其他.exe(安装版本,或直接来自PCbuild目录)时,推导出核心路径,并忽略注册表中的核心路径。始终读取注册表中的其他“应用程序路径”。当Python托管在另一个.exe(不同的目录,通过COM嵌入等)时,将不会推断出“Python Home”,因此使用了来自注册表的核心路径。始终读取注册表中的其他“应用程序路径”。
如果Python找不到它的主目录并且没有注册表值(冻结的.exe,一些非常奇怪的安装设置),那么你会得到一条带有一些默认但相对的路径的路径。
对于那些想要将Python捆绑到其应用程序或发行版中的人,以下建议将防止与其他安装冲突:
在您的可执行文件中包含一个
._pth文件,其中包含目录。这将忽略注册表和环境变量中列出的路径,并忽略site,除非列出import site。如果你在自己的可执行文件中加载
python3.dll或python37.dll,在Py_Initialize()之前,要显式调用Py_SetPath()或(至少)Py_SetProgramName()清除 和/或 覆盖
PYTHONPATH并在启动来自应用程序的python.exe之前设置PYTHONHOME。如果您不能使用前面的建议(例如,您是一个允许人们直接运行
python.exe的分发版),请确保安装目录中存在 landmark 文件 (Lib\os.py)。 (请注意,在 ZIP 文件中不会检测到该文件,但会检测到正确命名的 ZIP 文件。)
这些将确保系统范围安装中的文件不会优先于与应用程序捆绑在一起的标准库的副本。否则,用户可能会在使用您的应用程序时遇到问题请注意,第一个建议是最好的,因为其他建议可能仍然容易受到注册表和用户站点包中的非标准路径的影响。
在 3.6 版更改:
添加
._pth文件支持并从pyvenv.cfg中删除applocal选项当直接与可执行文件相邻时,添加
pythonXX.zip作为潜在的 landmark 。
3.6 版后已移除:
在
Modules(不是PythonPath)下的注册表中指定的模块可以通过以下方式导入importlib.machinery.WindowsRegistryFinder。在Windows上,此查找程序在3.6.0及更早版本的可用,但可能需要在将来显式添加到sys.meta_path
4.10. 附加模块¶
尽管Python的目标是在所有平台中都可移植,但是Windows有一些独特的特性。在标准库和外部都有一些模块和代码片段在使用这些特性。
特定于Windows的标准模块记录在 Windows系统相关模块 中。
4.10.1. PyWin32¶
Mark Hammond 的 PyWin32 模块是一组用于高级Windows特定支持的模块。这包括以下实用程序:
Component Object Model (COM)
Win32 API 调用
注册
事件日志
Microsoft Foundation Classes (MFC) user interfaces
PythonWin 是PyWin32附带的一个示例MFC应用程序。它是一个内置调试器的可嵌入IDE。
参见
- Win32 How Do I…?
Tim Golden 著
- Python and COM
David 和 Paul Boddie 著
4.10.2. cx_Freeze¶
cx_Freeze is a distutils
extension which wraps Python scripts into executable Windows programs
(*.exe files). When you have done this, you can distribute your
application without requiring your users to install Python.
4.11. 在Windows上编译Python¶
If you want to compile CPython yourself, first thing you should do is get the source. You can download either the latest release’s source or just grab a fresh checkout.
The source tree contains a build solution and project files for Microsoft
Visual Studio, which is the compiler used to build the official Python
releases. These files are in the PCbuild directory.
检查 PCbuild/readme.txt 以获取有关构建过程的一般信息。
有关扩展模块,请参阅 在 Windows 上构建 C 和 C++ 扩展 。
4.12. 其他平台¶
随着Python的不断发展,不再支持以前曾经支持的一些平台(由于缺少用户或开发人员)。检查 PEP 11 了解所有不支持的平台的详细信息。
Windows CE is no longer supported since Python 3 (if it ever was).
The Cygwin installer offers to install the Python interpreter as well
有关具有预编译安装程序平台的详细信息,请参阅 Python for Windows